Kafka
Overview
Apache Kafka is an open-source distributed event streaming platform. The project aims to provide a unified, high-throughput, low-latency platform for handling real-time data feeds.
Setting up Kafka
1. Add integration
Select Kafka from the integrations page.
2. Configure settings
Fill out the form with the following settings:
| Setting | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | TRUE | Name that will be displayed to users when selecting this integration in Superblocks |
| Brokers | TRUE | Comma-separated list of broker endpoints |
| SASL Mechanism | TRUE | Authentication mechanism. Choose between PLAIN, SCRAM SHA256, SCRAM SHA512 and AWS. |
| Username | TRUE | Username to connect to broker |
| Password | TRUE | Password for broker username |
| Enable SSL | FALSE | Connect via SSL if selected (SSL encryption should always be used if SASL mechanism is PLAIN) |
3. Test and save
Click Test Connection to check that Superblocks can connect to the data source.
If using Superblocks Cloud, add these Superblocks IPs to your allowlist (not necessary for On-Premise-Agent)
After connecting successfully, click Create to save the integration.
4. Set profiles
Optionally, configure different profiles for separate development environments.
Kafka Connected You can now consume and produce messages through Kafka in any Application, Workflow, or Scheduled Job.
Use Kafka in APIs
Once your Kafka integration is created, you can start creating steps in Application backend APIs, Workflows, and Scheduled Jobs. Kafka steps can be used to either Consume or Produce.
Learn more about building internal tools with streaming in our Streaming Applications guide.
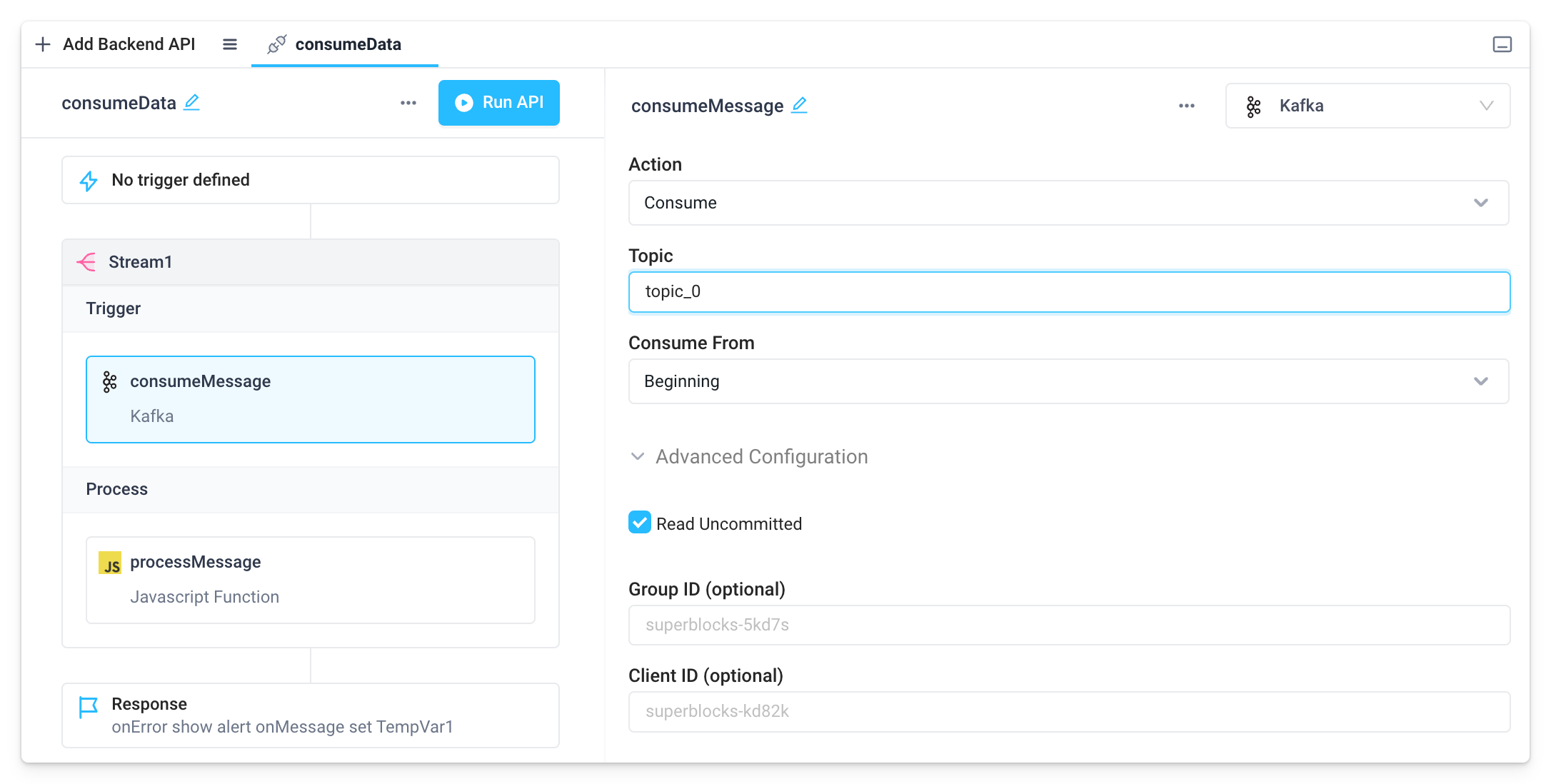
Consume
To consume data from Kafka:- Add a Stream block to your API
-
Add a block for your new Kafka integration with the action set to Consume
- Set the topic to consume from, how you want to consume, and any advanced settings desired
- Optionally, configure Process steps to process each message read off the stream
Produce
Write data to Kafka just by adding a step to your API using the Produce action.
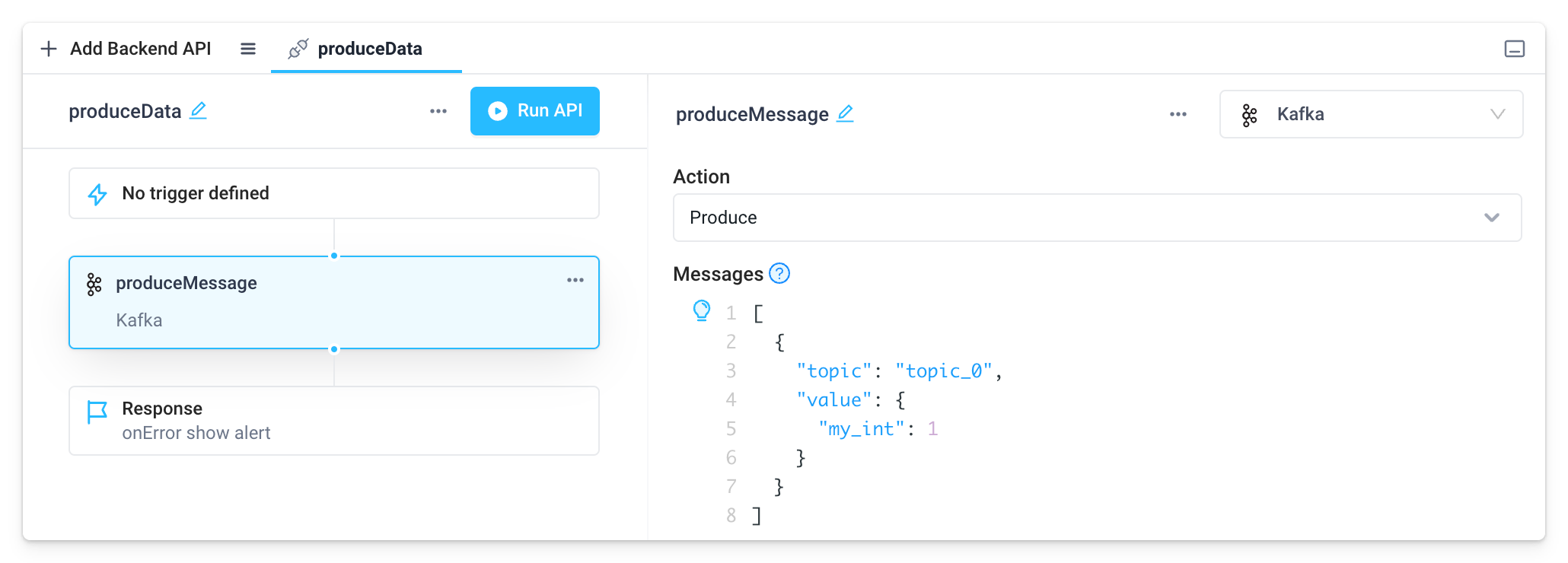
Superblocks supports JSON Schema formatted messages with the schema below. Schema Registry's are currently unsupported.
| Key | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
topic | True | The topic this record will be sent to. |
value | True | Record contents. |
partition | False | The partition that the record should be sent to. |
key | False | Key used to deterministically map messages to a partitions based on the hash of the key. |
timestamp | False | The timestamp of the record, in milliseconds since epoch. |
headers | False | Headers to be included with the record, sent as an Object with key-value pairs. |