Who can use this feature?
Organization Owners, Admins, and other users with the secrets:manage permission
- How to set up a new secret store connected to HashiCorp Vault
- Configuring and managing caching for your secret store to improve API performance
- Using secrets throughout the Superblocks platform
Prerequisites
To set up HashiCorp Vault as a secret store for Superblocks you’ll need:- An on-premises deployment of HashiCorp OR a HashiCorp account with Vault configured
- Permission to manage HashiCorp Services, access to manage HashiCorp Vault cluster, and ability to create and configure Secrets engines
Set up
Create Secrets Engine with secrets key-value pair
To set up a key-value secrets engine in HashiCorp Vault:- Navigate to your Vault Cluster
- Launch the Vault Web UI
- In the Vault Web UI, navigate to Secrets Engine
- Proceed to create a new secrets engine
- Choose KV Version. Opt for either version 1 or 2 of the Key-Value (KV) secrets engine, based on your requirements
- Add your secrets as key-value pairs
- Customize the path and configure access to your secrets as needed
Configure secret store
Finally, configure a new secret store in Superblocks:- Go to the Secrets Management page in Superblocks
- Click the HashiCorp Vault tile
- Name your secret store
- Paste or enter in the info for Address, Namespace, Path, Version, Auth Type, and Token configurations that were set in your Secrets engine
| Address | The Address is your cluster’s public URL. It is located on the Vault Cluster page when you select your Vault. |
|---|---|
| Namespace | The Namespace is used for creating service accounts and managing who can access what. The default value is admin. It is optional and configured on the secrets engine. |
| Path | The Path tells Vault which secrets engine it should route requests to. It is configured in the Key Value secrets engine. |
| Version | The Version is which version of Key Value secrets engine to use (either v1 or v2 currently). It is configured in the Key Value secrets engine. |
| Auth Type | The Auth Type specifies which Auth flavor to use for connecting to HashiCorp Vault. The default configuration is Token. App Role is also available which requires a Role ID and Secrets ID. |
| Token | The Token is used to authenticate requests for secrets. It is located on the Vault Cluster page when you select your Vault. |
- Configure caching rules for this store
- Optionally, add more configurations for different environments
- Click Create
Your secret store is now configured. Developers can now reference secrets in their backend APIs and integrations.
Caching
If enabled, Superblocks can cache your secrets, reducing calls to your secrets manager and improving API performance when using secrets. Caching can be configured for each of your secret store’s configurations, letting you set different policies based on the environment. To configure caches, go to Secrets Management and click into your secrets store. From here you can:- Update the Cache TTL (seconds) to your desired caching interval
- Clear the cache if you’ve rotated a secrets and need Superblocks to refetch secret values
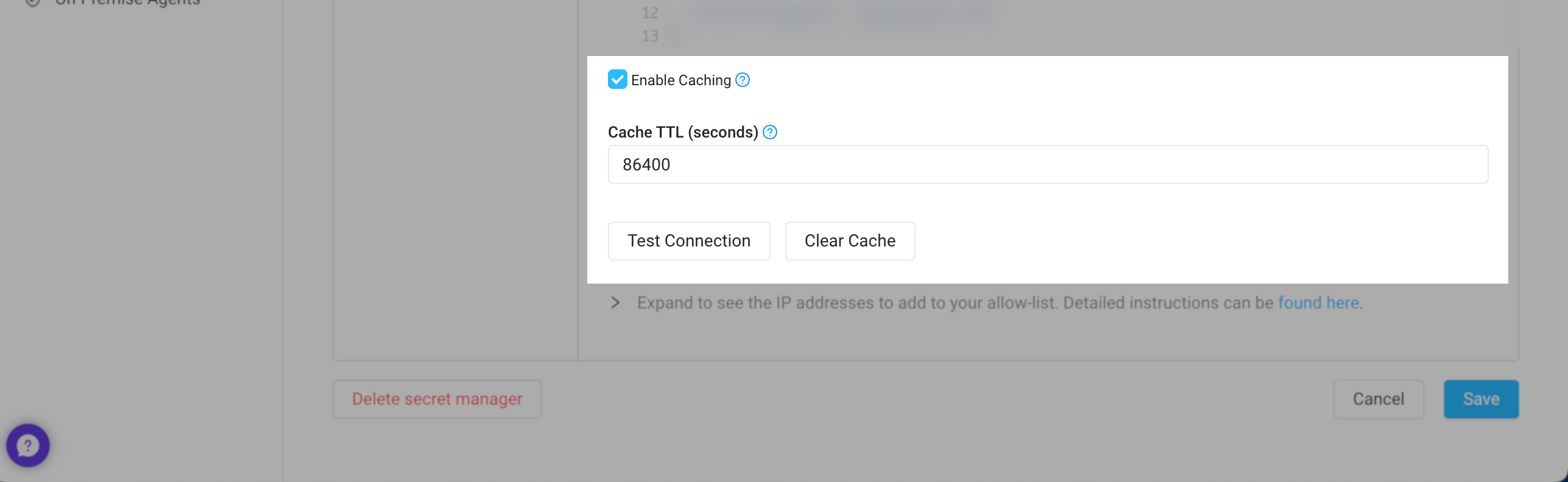
If you’re self-hosting with Hybrid or Cloud-Prem architectures, secrets are cached in-memory by the data plane. For scaled deployments, you’ll need to clear each instance’s cache individually when rotating secrets. To rotate secrets more easily, disable caching first. Then, after updating the secret, re-enable caching.
Auth token renewal
When using the token auth type for accessing the configured secret store, if the configured token is renewable, it will be renewed every time the secret store is accessed. For the token to be renewed it must:- Be renewable (i.e. the “renewable” attribute is true)
- Have permissions to renew itself
- Not be expired
Note: If the access token has a max TTL set on it, the renewed TTL will be capped so that the token’s total lifetime never exceeds the max TTL.
E.g. Given a token with an initial TTL of 4 minutes and a max TTL of 5 minutes, if the token is renewed after 3 minutes (1 minute remaining), the TTL will be reset to 2 minutes (not 4 minutes)
E.g. Given a token with an initial TTL of 4 minutes and a max TTL of 5 minutes, if the token is renewed after 3 minutes (1 minute remaining), the TTL will be reset to 2 minutes (not 4 minutes)
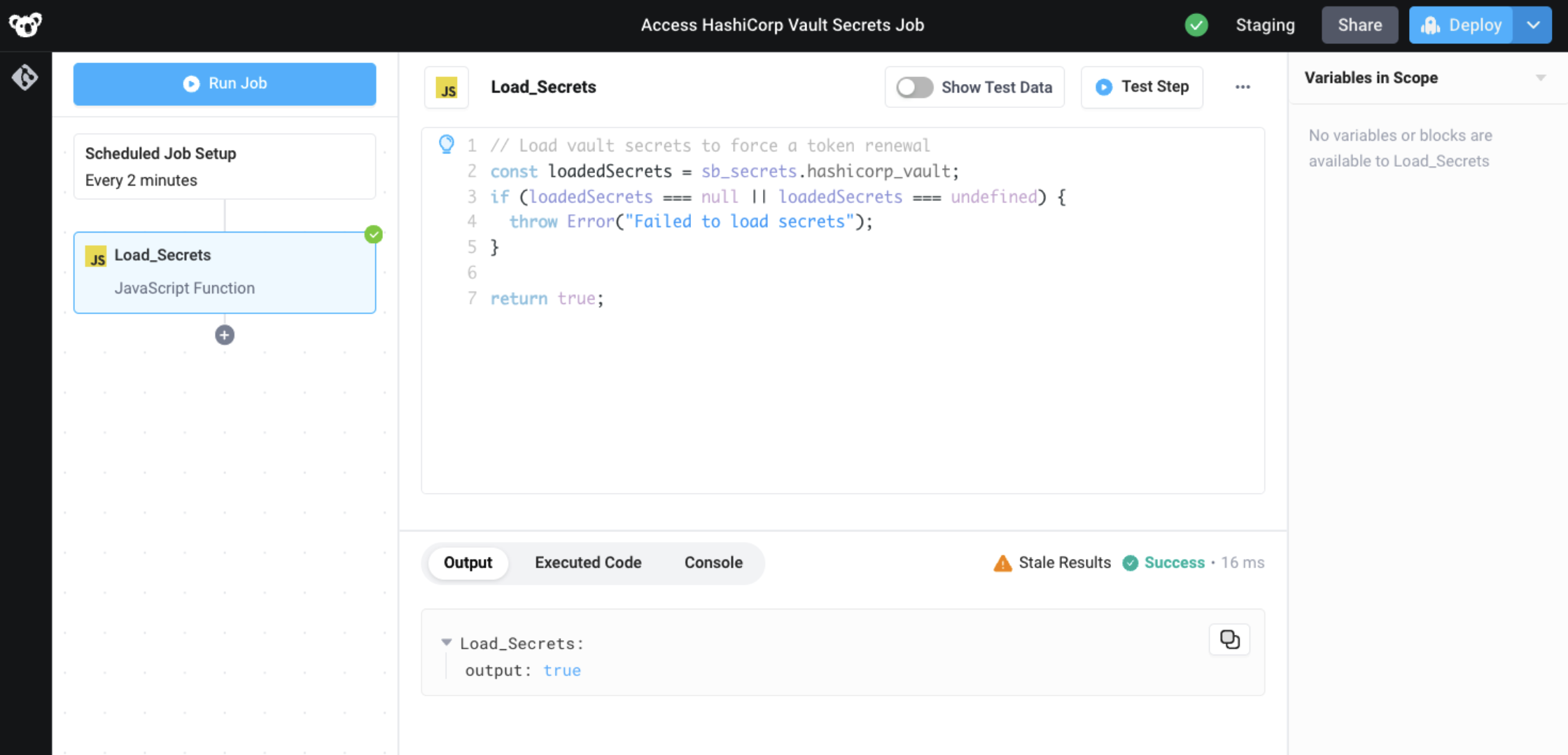 A scheduled job with a single JavaScript step, containing the following code, can be used to ensure the secret store is always accessed within the TTL of the access token.
A scheduled job with a single JavaScript step, containing the following code, can be used to ensure the secret store is always accessed within the TTL of the access token.




